TYPES OF DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS
Revolutionizing Bone Lengthening and Facial Reconstruction: The Power of Distraction Osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis (DO) is a surgical marvel harnessing the body’s natural bone-regeneration capacity to reshape and lengthen bones. This groundbreaking procedure involves a meticulous bone cut, implanting a distractor device, and gradually separating bone segments to stimulate new bone formation. DO has transformed the treatment landscape for diverse conditions:
1. Limb Lengthening: DO effectively lengthens limbs, particularly in children with congenital deformities or growth disorders, offering controlled and precise lengthening over time.
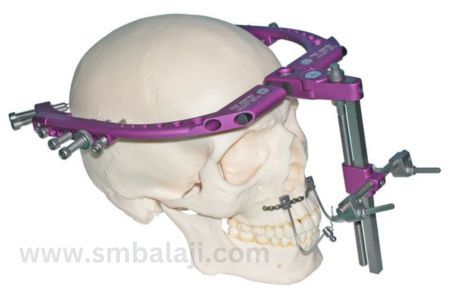
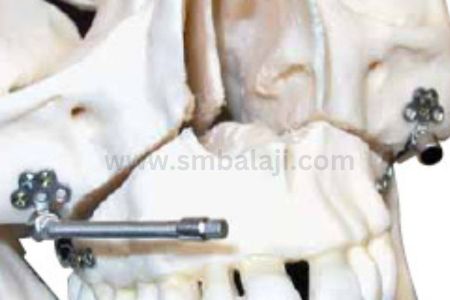
2. Facial Reconstruction: Crucial in treating craniofacial deformities, DO reshapes facial bones, like the mandible or maxilla, achieving a harmonious facial structure.
3. Non-Union Fractures: DO proves effective in treating non-union fractures by stimulating new bone growth through gradual separation of fracture fragments.
4. Bone Grafting Elimination: DO eliminates the need for traditional bone grafting, stimulating new bone formation directly at the treatment site and avoiding associated complications.
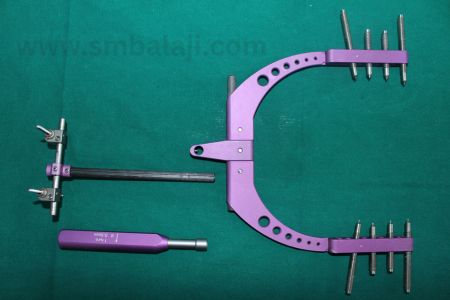
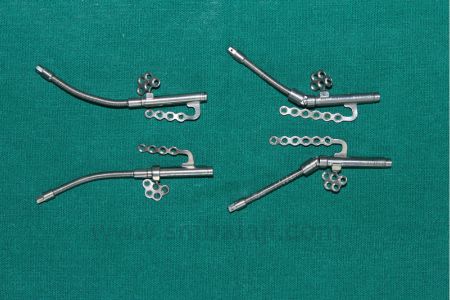
Types of Distraction Osteogenesis Devices:
External Distractors: Attached externally with pins or screws, ideal for lengthening long bones like the femur or tibia.
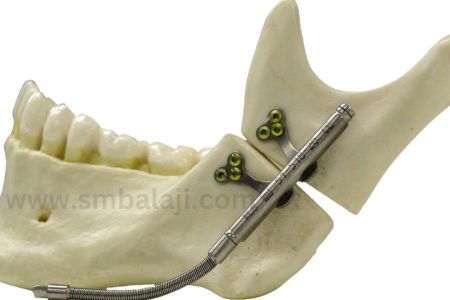
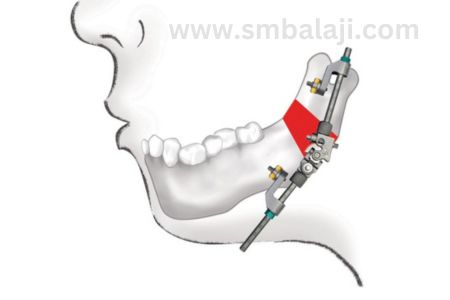
Internal Distractors: Concealed within bones, suitable for facial reconstruction and cases where external distractors are impractical.
Hybrid Distractors: Combining external and internal elements, offering versatility and control in the distraction process.
Procedure Overview:
Preoperative Planning: Crucial for determining distraction vector, device type, and treatment duration.
Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, bone cut and distractor device implantation occur, securing the device to bone segments.
Distraction Phase: Gradual activation of the distractor device, controlled bone separation, and lengthening.
Consolidation Phase: Halting distraction, allowing bone segments to consolidate and heal; device removal post-consolidation.
Follow-up Care: Regular visits monitor healing and ensure proper bone formation.
Advantages of Distraction Osteogenesis:
Minimally Invasive: Reduces infection, scarring, and blood loss compared to traditional techniques.
Precise and Controlled: Ensures accurate bone lengthening or repositioning.
Eliminates Bone Grafting: Avoids associated risks and complications.
Promotes Natural Regeneration: Stimulates the body’s natural bone-regeneration ability, resulting in durable bone formation.
Improved Comfort and Recovery: Often leads to enhanced patient comfort and faster recovery compared to traditional methods.
Distraction can be classified in different ways.
- According to the site where it is used, it can be classified as mandibular (lower law), maxillary (upper jaw), alveolar (in teeth bearing region of the jaws), palatal (roof of the mouth) or craniofacial (skull).
- Facial bones are unique. They are not straight, so they may be needed to be moved in more than one direction to achieve the desired results. According to the direction of bone movement, distraction may be univector (bone moved in one direction), bivector (bone moved in two directions) or multivector (bone moved in multiple directions).
- According to the placement of the distractor, it is classified as Intraoral and Extraoral.
- According to anchorage it may be fixed to teeth (teeth borne) or fixed to bone using plates or screws (bone borne)
- According to the age for which it is designed, distractors can be either paediatric or adult.