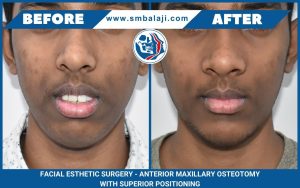
[vc_section content_layout=”full” animation_delay=”” disable=”” id=”” class=”” bg_type=”image” bg_image=”” color_overlay=”” enable_parallax=”” enable_pattern=””][vc_row content_layout=”boxed” equal_height=”” animation_delay=”” disable=”” id=”” class=”” bg_type=”image” bg_image=”” color_overlay=”” enable_parallax=”” enable_pattern=””][vc_column layout=”normal” vertical_align=”top” animation_delay=””][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”What is hemifacial microsomia” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Hemifacial microsomia is a congenital disorder, which mostly affects the development of the face. A congenital disorder is a disease condition that exists at the time of birth. The lower half of the face including the lower jaw and the ears are affected the most. There is a small jaw and rudimentary external ears. At times, it is so severe that the external ears are just skin tags. Ear reconstruction is best performed after 10 years of age. It usually affects only one side of the face and is rarely bilateral. The rudimentary ears need ear reconstruction surgery with cartilaginous grafts from the ribs.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Rudimentary external ear or microtia correction surgery” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Microtia surgery is performed by only a few experienced surgeons. It is a very difficult surgery that requires years of experience to master. It is a three step surgery. During the first surgery, the cartilaginous rib grafts are crafted and shaped according to a template that is obtained from biometric study of the patient’s face. This is a procedure that requires a great deal of artistic skill since the graft has to be crafted to be symmetrical to the patient’s normal ear.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”The three steps of successful ear reconstruction surgery or cosmetic ear surgery” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]This graft is first placed in a skin pocket created in the region of the patient’s external ear. This is allowed to mature. The second and the third stages of the procedure involve lifting up the cartilaginous graft using skin flaps so that it perfectly mimics the patient’s normal ear in structure. Children who undergo this procedure are ecstatic at seeing the results of the procedure as they have always felt self conscious, fearing comments from other children.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Effects of hemifacial microsomia on the quality of life of the patients” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Disability from hemifacial microsomia is at many levels. The facial asymmetry also results in the patient withdrawing into a shell, shying away from all social contact. Absence of an external auditory canal is one of the symptoms of hemifacial microsomia. It is also a feature of craniofacial microsomia. Hearing loss is a common presentation in this presentation. Bony conduction of hearing is however present in a majority of cases. The use of cochlear implants greatly enhances the patient’s ability to hear.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Static or dynamic smile recreation surgery through fascia lata graft” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Patients suffering from hemifacial microsomia also have an asymmetrical mouth. A beautiful smile is the ornament of a vibrant personality. The asymmetrical mouth makes them very self conscious and they tend to avoid eye contact with other people. This can be rectified through judicious performance of facial reanimation surgery. A strip of fascia lata graft is first harvested from the thigh.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Transformation in the life of patients after facial reanimation surgery” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]This strip of fascia lata is used as a graft to connect the labial commissure of the affected side of the mouth to a dynamic muscle, which when activated results in a beautiful smile. The fascia lata graft is tunneled from the muscle to the angle of the mouth and anchored in place using sutures. This is a life changing surgery and patients undergoing this have a transformed personality due to regaining their ability to smile, which enables them to connect with others.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Jaw reconstruction surgery for correction of asymmetrical mandible” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Jaw correction is achieved through mandibular distraction osteogenesis by the use of distraction devices on the affected side. Plastic reconstructive surgery (plast reconstr surg) is the surgery of choice for correction of the facial asymmetry that results from hemifacial microsomia. Correction of soft tissue defects is through the use of fat grafts. Le Fort I osteotomy is performed when there is involvement of the maxilla in craniofacial microsomia. Use of bone graft in deficient bone segments is used to correct any residual facial asymmetry after completion of the osteotomy.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Patient with long standing facial asymmetry due to hemifacial microsomia” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]The patient is a young man from Solapur, Maharashtra. He had begun noticing a facial asymmetry a few years ago that had developed gradually. He had also progressively developed difficulty with chewing and speech. This problem was slowly turning debilitating and his quality of life had significantly declined. He had habitually started tilting his head to the left side to conceal his facial asymmetry from other people. This had resulted in severe spasms of his neck muscles. The spasms were very painful and had begun to affect his sleeping cycle. This chronic lack of sleep had begun to affect all walks of his life including his work life.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Patient and parents seek medical help to help the patient” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]He and his parents approached a local oral surgeon for diagnosis and treatment due to the severe neck pain. It was explained to them that the patient had a high degree of facial asymmetry with a skewed occlusal cant. He diagnosed the patient as having hemifacial microsomia. The patient required facial asymmetry correction surgery. It was explained to them that facial asymmetry surgery in India was performed only in a few specialty centers. The patient and his parents were then referred by him to Balaji Dental and Craniofacial Hospital in Chennai, India.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Treatment planning explained and consent obtained for distraction osteogenesis” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Dr SM Balaji examined the patient and ordered detailed imaging studies including a 3D CT scan. Biometrics were then obtained, which revealed a 10 cm shortening of the ramus on the left side when compared to the right. It was decided to proceed with simultaneous maxillary and mandibular distraction for the patient. The treatment planning was explained in detail to the patient and his parents who consented to the surgery.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy of the mandible” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Under general anesthesia, a sagittal split osteotomy was performed on the left mandibular ramus. A Univector ramus distractor was then fixed with screws to the distracted segments of the mandible. Functioning of the distractor was checked before the incision was closed with sutures.
Attention was next turned to the maxillary distraction. A vestibular incision was performed followed by a Le Fort I maxillary osteotomy. Dysjunction of the maxilla was then performed on the left side followed by stabilization of the distracted segments.[/vc_column_text][vu_heading style=”2″ heading=”Establishment of facial symmetry through distraction osteogenesis” subheading=”” alignment=”left” custom_colors=”” class=””][vc_column_text]Distraction osteogenesis of the mandible would be performed after a latency period of seven days to allow for stabilization of the distracted site. This will be followed by a distraction of 1 mm everyday for a total of 10 mm of distraction in ten days. The distractors would be left in place for a period of three months for the new bone to consolidate at the distracted site. Consolidation of the new bone is confirmed by establishment of normal trabecular pattern at the site of new bone formation. The distractors are removed once the trabecular pattern of the new bone and old bone become indistinguishable.
This would result in establishment of facial symmetry for the patient. The patient and his parents expressed their satisfaction at the results of the surgery before final discharge from the hospital. Parents of the patient said that they could already see that the patient was very excited about facing the future after undergoing this life changing surgery.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][/vc_section]