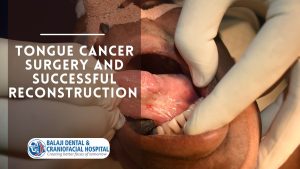
Patient sustains a facial injury from a two wheeler accident
The patient is a 36-year-old male from Madurantakam in Tamil Nadu, India. He was on his way to work on his two-wheeler when he hit a coconut lying on the road. This caused him to skid and lose balance. He fell down on the right side of his face on a grassy area by the roadside. There was direct impact on the cheek region.
Passersby immediately rushed him to a nearby hospital where x-rays were taken. The patient was diagnosed with a right zygoma fracture by the duty doctor there. He had then been referred to our hospital for surgical management of his facial fracture.
He was not wearing a helmet at the time of the accident. It was explained to the patient that wearing a full face helmet would have prevented the fracture.
Occurrence of zygomatic fracture and associated symptomatology
Zygoma fracture is a form of facial fracture caused by a fracture to the zygomatic bone. This often results from facial trauma such as violence, falls or automobile accidents. Symptoms include flattening of the face, trismus (reduced opening of the jaw) and subconjunctival hemorrhage.
It has been scientifically proven through the use of crash test dummies that helmets prevent facial and head injuries. Statistics prove that 99% of head injuries occur in riders without helmets. It is a laudable initiative by the government to educate the public towards road safety awareness through the use of helmets.
There is scientific evidence that the chances of the pillion rider suffering fatal injuries are very high. It is therefore imperative that the pillion rider too wears a helmet.
Initial presentation at our hospital for treatment
Dr SM Balaji, facial trauma surgeon, examined the patient and obtained a detailed history. The patient complained of a depression on the right side of the face along with pain, swelling and limitation of function. He stated that he was very upset by the facial asymmetry that had been caused by the accident.
A complete clinical and radiological evaluation was done. Clinical examination revealed a depressed right zygoma. Radiographic examination revealed depressed right zygoma, zygomatic arch and frontozygomatic fracture. This is the classical fracture pattern caused by impact in the zygomatic region from road traffic accidents.
The findings were explained to the patient in detail. He was advised to undergo zygoma fracture reduction and fixation through an intraoral approach. This would avoid any unsightly extraoral scarring. The patient was also advised to take liquid diet for about 1-2 weeks followed by a semi-solid diet.
Successful rehabilitation of the fracture and return to normalcy
Under general anesthesia, a sulcular incision was made in the right maxillary vestibular region and a flap was raised. Dissection was made to the region of the zygomatic fracture. The depressed right zygoma fracture segment was identified, reduced and stabilized using titanium plates and screws. The closure was done using resorbable sutures intraorally.
Surgery was successful with no postoperative complications. Results were immediate. The patient was greatly satisfied with the outcome of the surgery.
There was no residual facial depression and his face was now symmetrical on both sides. He expressed his happiness to the surgical team.